English Grammar Launch Advanced is an advanced English grammar course taught by me, Anthony, a native British English speaker. You will learn the target English grammar structures at a deep level, so that you can sound more native-like when you speak English.
This course includes:
- lectures for the target structures
- speaking practice for every single grammar structure
- listening practice for every single grammar structure
- future updates – this course will continue to grow and grow
- PDF transcripts
- and MP3 downloads so that you can learn anywhere, any time.
Each section focuses on one, two or three target structures so that you can master each one and produce it accurately in your spoken English.
This course is extremely detailed, so you can fully master the target English.
If you want to speak English more clearly, if you want to sound more native-like, or if you simply want to take your English to an advanced level, this course can help you achieve your goal of taking your English to the next level.
What you’ll learn
- Understand more advanced spoken English.
- Have a deeper knowledge of the structure of advanced English grammar.
- Speak English with more confidence.
- Produce the target structures confidently and accurately.
- Sound more fluent by using advanced English.
Course content
TEACHER
Hello there.
My name is Anthony, and I’m from London, England. I have almost half a million students enrolled on my Udemy courses, which focus on learning English as a foreign language. My courses have some of the highest ratings on Udemy.
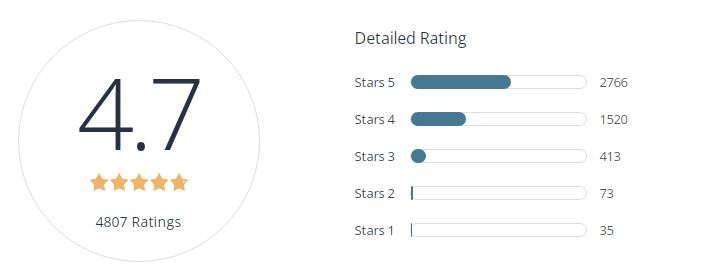
REVIEW
1. Affirmative (+)
The future tense takes two general forms:
Subject + be going to + verb
- Ex: The exam is going to begin at noon
Subject + will + verb
- Ex: The exam will begin at noon.
2. Negative (-)
Subject + be going to + verb
- Ex: I am not going to the Market tomorrow
Subject + will + not + verb
- Ex: We will buy this product any more
3. Interrogative (?)
Will + Subject + verb?
- Ex: Will we buy a special pen for the final exam?
Be + Subject + going to + verb
- Ex: Are we going to the beach next week>
———————————————
II. How to use
- For a future plan
- Ex: I am going to go to the beach next weekend.
- Ex: I will go to the beach next weekend.
- Ex: The race is going to be one of the most exciting of the year!
- Ex: The race will be one of the most exciting of the year!
- For a prediction
- Ex: In the next decade, electronics are going to decrease in price.
- Ex: In the next decade, electronics will decrease in price.
- Ex: Small pets are going to be much more popular as people move into big cities.
- Ex: Small pets will be much more popular as people move into big cities.
The post The Simple Future Tense (Example & Explanation)| English Grammar first appeared on Helena Daily English.]]>
I. Form
1. Affirmative (+)
Subject + have/has + Past Participle
Ex: I have worked for 4 years in the USA
2. Negative (-)
Subject + have/has + Past Participle
The negative of have in present perfect is have not/has not. The contractions haven’t for have not and hasn’t for has not are not common in academic writing.
Singular
- I have not walked
- You have not walked
- He / She / It has not walked
Plural
- We have not walked
- You have not walked
- They have not walked
Sentences containing the verb have as the main verb may look odd in the present perfect. However, this construction is correct.
Ex: I have had many great cups of espresso since I arrived here in Italy.
3. Interro-Negative (?)
Have/has + Subject + Past Participle
Ex: Have you ever visited the USA yet?
———————————————
II. How to use
Uses of the Present Perfect
- For an action that started in the past and continues in the present (This particular use often includes the phrases “since+ a specific time” or “for+ length of time”)
- Ex: California has been a state since 1850.
- Ex: California has been a state for more than 150 years.
- For an action that has just been completed (often using just)
- Ex: We have just finished working.
- For a past action that still has an effect on the present
- Ex: The company lost revenue, so management has fired many employees.
- For an action that happened several times (no specific past time) and may happen again (indefinite past)
- Ex: We have eaten at that restaurant five times.
- For an action that happened in the past, but the time or frequency of the action is not important (often used with ever or never)(indefinite past)
- Ex: Julia has never visited Las Vegas, but she would like to.
- Ex: Have you ever driven an Italian sports car?
Notes on the Past Participle
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Read more: Regular and Irregular Verbs List (Full) from Cambridge Dictionary
The post The Present Perfect Tense (Example & Explanation)| English Grammar first appeared on Helena Daily English.]]>
Sometimes you can look at a word and guess its part of speech. For example, if a word ends in -tion or -ation, it is probably a noun.
- Ex: (a) The teacher’s selection of questions is usually good.
- Ex: (b) The action of the police was very rapid.
- Ex: (c) The teacher will give us an examination
If you want to use these three words as verbs instead of nouns, you must change the word form. The verb forms are select, act, and examine.
- Incorrect: (d) The teacher selections good questions.
- Correct: (e) The teacher selects good questions.
Why is (d) wrong? Why is (e) correct?
The answer is that you must use a verb form, not a noun form.
Here are four examples of useful word formation patterns:
- verb + -(a)tion -> noun select -> selection
- verb + -able -> adjective chew -> chewable
- verb + -ment -> noun announce -> announcement
- adjective + -ly adverb slow slowly
The post Learn English Grammar: Lesson 8 – Word Forms first appeared on Helena Daily English.]]>Learn English Grammar: Lesson 9,10 – Noun Basics, Count Nouns
A conjunction is a word that connects parts of a sentence together.
In the middle of a sentence: and, but, or, so
- Ex: Central America includes Nicaragua, Guatemala, and Honduras.
- Ex: At this school, students can study Japanese or Chinese.
- Ex: He travels for his job, so he is often out of town.
In the middle OR at the beginning: because, although, when, before, after
- Ex: He speaks Spanish because he is from Mexico.
- Ex: Because he is from Mexico, he speaks Spanish.
- Ex: The car had problems before I bought it.
- Ex: Before I bought the car, it had problems
The post Learn English Grammar: Lesson 7 – Conjunctions first appeared on Helena Daily English.]]>
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or pronoun.
Adjectives: good, delicious, happy, interesting, important, serious, green, cold, many, Mexican, French, English, Chinese, difficult, clean, six
Adjectives answer the questions “Which?” “How many?” “What kind?” For example, this sentence has three adjectives:
Ex: My white cat sometimes eats two pieces of fried chicken.
Which cat? How many pieces? What kind of chicken?
In English, adjectives can come after be or before nouns.
- after be: Ex: Canada is big.
- before noun: Ex: Canada is a big country.
- after be: Ex: Elvis Presley was very popular.
- before noun: Elvis Presley was a very popular singer.
The post Learn English Grammar: Lesson 5 – Adjectives first appeared on Helena Daily English.]]>